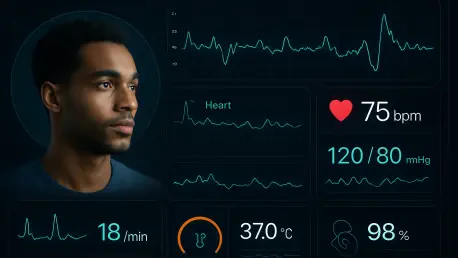
Imagine a hospital emergency room where doctors can predict a patient’s risk of cardiac arrest before symptoms even fully manifest, thanks to a stream of real-time data from wearable devices and integrated medical records. This isn’t a distant dream but a reality in many health systems today, where data is becoming the cornerstone of intelligent, proactive care. The ability to analyze and act on information instantly is transforming healthcare, enabling better patient outcomes, streamlined operations, and significant cost savings. Real-time health system intelligence, powered by vast datasets, is redefining how providers anticipate needs and deliver solutions. This guide explores best practices for leveraging data to achieve these advancements, offering actionable insights for health systems aiming to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving landscape.
The Importance of Real-Time Data Intelligence in Healthcare
Real-time data intelligence stands as a critical tool for modern healthcare, where split-second decisions can mean the difference between life and death. By processing information as it emerges, health systems can shift from merely reacting to crises to preventing them altogether. This capability allows for immediate interventions, such as adjusting treatments based on live patient metrics, ensuring that care is both timely and precise. The urgency of adopting such systems cannot be overstated, as they empower providers to address issues before they escalate into emergencies.
Beyond individual patient care, real-time intelligence optimizes broader operational aspects. Hospitals can allocate resources like staff and equipment more effectively by analyzing current demand trends, reducing wait times and enhancing service delivery. Moreover, this approach supports public health by enabling rapid responses to outbreaks, ensuring communities are protected through swift action. The overarching benefit lies in moving toward a preventive model, where data-driven insights help avert hospital readmissions and chronic condition flare-ups.
The transformative power of this technology also extends to cost efficiency, a pressing concern for many institutions. By identifying high-risk patients early and tailoring interventions, health systems can minimize expensive emergency visits and prolonged stays. This guide delves into specific strategies that make these outcomes possible, providing a roadmap for integrating data intelligence into daily operations while balancing innovation with essential safeguards like privacy.
Best Practices for Leveraging Data in Real-Time Health Intelligence
Integrating Data Through Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
A foundational best practice for real-time intelligence is the seamless integration of data via Electronic Health Records (EHRs). These digital systems compile patient information from diverse sources—hospitals, laboratories, and even personal wearables—into a unified platform. This consolidation offers providers a comprehensive view of a patient’s health, enabling continuous monitoring and immediate action when anomalies are detected.
EHRs play a pivotal role in facilitating early interventions by alerting clinicians to critical changes in patient status. For instance, in managing chronic conditions, these records ensure that data from multiple touchpoints is accessible in one place, allowing for coordinated care plans. Health systems adopting this practice should prioritize interoperability, ensuring that different EHR platforms can communicate effectively to avoid data silos that hinder real-time responses.
A practical example is seen in diabetes care, where EHRs track blood sugar readings in real time, sending alerts to providers if levels become dangerously high or low. Such systems prevent emergencies by prompting timely adjustments to medication or diet. To implement this effectively, organizations must invest in user-friendly interfaces and train staff to navigate EHRs efficiently, maximizing their potential for patient benefit.
Harnessing Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning
Another essential practice involves deploying predictive analytics and machine learning to anticipate health trends and needs. These technologies sift through massive datasets to identify patterns, forecasting outcomes like disease progression or resource shortages. By doing so, they enable health systems to prepare for future challenges rather than merely addressing current ones.
The application of these tools is particularly impactful in identifying patients at high risk of complications. For example, algorithms can analyze historical data to flag individuals likely to experience hospital readmissions, allowing for targeted follow-up care. Health systems should focus on integrating these models into existing workflows, ensuring that predictions translate into actionable steps without overwhelming clinical staff.
To maximize effectiveness, collaboration with data scientists is recommended to tailor algorithms to specific patient populations. Regular updates to these models are also crucial, as they must adapt to evolving health trends. When implemented thoughtfully, predictive analytics not only enhances individual care but also streamlines resource allocation, ensuring that critical support reaches those who need it most.
Real-Time Surveillance for Public Health Crises
Implementing real-time surveillance systems is a vital best practice for managing public health threats at a community level. By aggregating data from hospitals, clinics, and public reports, these systems detect early signs of outbreaks, such as unusual spikes in illness cases. This rapid identification allows authorities to mobilize resources and contain issues before they spiral into widespread crises.
Such surveillance is particularly effective in directing aid to high-need areas, ensuring that interventions are both timely and targeted. Health systems should establish partnerships with local and national agencies to share data seamlessly, creating a robust network for monitoring. Additionally, investing in dashboards that visualize trends can help decision-makers act with clarity and speed during emergencies.
A notable instance of this practice in action occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic, where real-time tracking of case surges guided the distribution of ventilators and vaccines. To replicate this success, health systems must prioritize scalable surveillance tools that can handle large data volumes without lag. Regular testing of these systems ensures reliability, safeguarding public health against unforeseen challenges.
Advancing Care with Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
Telehealth and remote monitoring represent a forward-thinking practice for delivering care beyond traditional settings. These tools collect real-time data from patients using devices like glucose monitors or blood pressure cuffs, feeding information directly into health systems for analysis. This approach is especially valuable for managing chronic conditions, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
Accessibility is a key advantage here, as patients in rural or underserved areas can receive consistent care without travel burdens. Health systems should focus on integrating telehealth platforms with EHRs to ensure data continuity, while also providing technical support to patients unfamiliar with digital tools. Clear communication protocols for virtual consultations further enhance the patient experience.
For instance, remote monitoring of heart failure patients allows providers to adjust treatments based on live vital signs, preventing exacerbations. To adopt this practice effectively, organizations must address barriers like internet access disparities by offering alternative solutions such as phone-based check-ins. Training clinicians to interpret remote data accurately is equally important, ensuring that virtual care matches the quality of in-person interactions.
Population Health Management Through Data Analytics
Using data analytics for population health management is a strategic practice that tackles systemic health challenges. By examining large-scale data, health systems can uncover disparities tied to social determinants such as income or education, which often influence care access. This insight enables the design of interventions that address root causes rather than just symptoms.
Tailored programs based on these findings can significantly improve community outcomes, such as reducing chronic disease prevalence in underserved areas. Health systems should collaborate with community organizations to gather relevant data and ensure interventions are culturally sensitive. Transparent reporting of progress also builds trust among stakeholders, encouraging sustained participation.
An effective application involves targeting high-risk neighborhoods with mobile clinics or health education campaigns, directly addressing identified gaps. To implement this, a multidisciplinary approach involving public health experts and data analysts is recommended. Continuous evaluation of program impact through data ensures that efforts remain aligned with evolving community needs, fostering long-term health equity.
Prioritizing Data Security and Privacy
As data usage grows, prioritizing security and privacy emerges as a non-negotiable best practice. Protecting patient information through robust measures like encryption and access controls prevents breaches that could erode trust. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA is essential, ensuring that legal standards are met while handling sensitive data.
Health systems must also invest in regular staff training to mitigate risks like phishing or unauthorized data sharing. Conducting routine audits of security protocols helps identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited. A culture of accountability, where every team member understands their role in safeguarding data, is critical to maintaining integrity across operations.
Consider a scenario where advanced cybersecurity measures thwarted a potential breach, preserving patient confidentiality and system reliability. To achieve similar outcomes, health systems should partner with IT specialists to stay updated on emerging threats. Transparent communication with patients about data protection practices further reinforces confidence, ensuring that innovation does not come at the expense of privacy.
Final Thoughts on Data-Driven Health Intelligence
Reflecting on the journey through these best practices, it becomes clear that data has fundamentally reshaped healthcare delivery by enabling real-time intelligence. Each strategy, from EHR integration to telehealth expansion, has demonstrated its capacity to enhance patient care and operational efficiency. The emphasis on security and privacy has also proven indispensable, ensuring that trust remains at the core of technological advancements.
Looking ahead, health systems are encouraged to take bold steps by piloting one or more of these practices, starting with areas of greatest need within their operations. Collaborating with technology providers to customize solutions offers a practical pathway to adoption, while seeking grants or partnerships can ease financial constraints. Engaging staff and patients in the transition process has shown to be a vital component, fostering acceptance and maximizing impact.
Ultimately, the focus shifts to building a sustainable framework where data intelligence can evolve with emerging trends. Exploring innovations like artificial intelligence for deeper insights or blockchain for enhanced security presents exciting opportunities. By committing to continuous learning and adaptation, health systems position themselves to not only meet current demands but also anticipate future challenges, ensuring a healthier tomorrow for all.