In the intricate digital tapestry of daily life, few things are more universally frustrating than when a core piece of technology, like the phone app, behaves unpredictably during a critical moment. The Google Phone app represents a significant advancement in the core user experience for the Android ecosystem. This review will explore the evolution of a recent update, its key features, performance metrics, and the impact it has had on user interaction. The purpose of this review is to provide a thorough understanding of the update, its current capabilities, and its potential for future development in user-centric design.
The Accidental Rotation Problem
The introduction of landscape mode to the Phone app, while intended as a feature, inadvertently created a significant usability issue for many users. The core principle of the problem emerged after a previous update enabled the in-call screen to shift orientation based on the device’s position. For users with system-wide auto-rotate enabled, a slight tilt of the handset during a conversation would cause the interface to flip, leading to a jarring and disorienting experience.
This seemingly minor change quickly became a common frustration point within the broader Android user base. The issue was most pronounced when users attempted to end a call; as they brought the phone down from their ear, the screen would often rotate, displacing the end-call button from its familiar bottom-center position. This forced users to reorient their grip or hunt for the button, turning a simple action into a moment of aggravation and inefficiency.
A Closer Look at the Solution
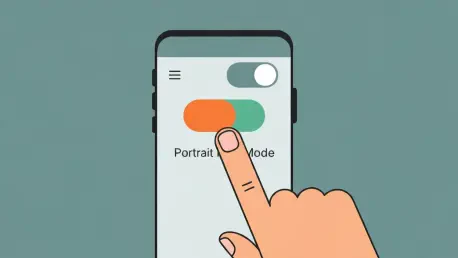
The Keep Portrait Mode on Calls Toggle
In response to widespread user feedback, the update’s primary solution is a new toggle switch that gives users direct authority over screen orientation during calls. This function, precisely located within the app at Settings > Display options, allows individuals to lock the in-call screen in portrait mode. Its implementation is both simple and effective, disabling rotation for the Phone app without requiring users to deactivate the system-wide auto-rotate setting, thereby solving the core problem without creating a new inconvenience.
The significance of this toggle extends beyond its immediate function. It represents a targeted, granular approach to problem-solving, empowering users with the choice to opt out of a feature that disrupts their workflow. By adding this control, Google acknowledged that a one-size-fits-all design does not always work for an application as fundamental as the phone dialer, providing a tailored experience that respects individual user preferences.
Refinements to the User Interface
Another key component of the update involves subtle yet meaningful aesthetic and functional improvements to the user interface. Alongside the orientation fix, developers introduced a shorter bottom bar within the app. While a minor adjustment, this change modernizes the app’s appearance, creating more screen real estate and contributing to a cleaner, less cluttered visual presentation.
These small modifications work in concert with the main feature to enhance the app’s overall usability and deliver a more polished user experience. Such refinements demonstrate an attention to detail that goes beyond just fixing bugs. They show a commitment to improving the holistic feel of the application, ensuring that functional enhancements are paired with a visually appealing and intuitive design.
The Shift Toward User Driven Features
This update highlights an emerging trend in Google’s app design philosophy: a greater willingness to respond directly to user feedback and community complaints. The implementation of the portrait mode toggle is a clear example of developers listening to the end-user and providing a specific solution to a widely reported problem. This move is indicative of a broader strategic shift within the company’s software development process.
This shift from a top-down, one-size-fits-all approach to offering granular, user-controlled settings is influencing the technology’s trajectory. Instead of assuming what features users will find beneficial, the new paradigm involves building more flexible applications that can be customized to fit diverse needs and habits. Consequently, the development cycle is becoming more iterative and collaborative, with community input playing a vital role in shaping future updates.
Practical Applications and User Impact
The real-world applications of this seemingly small update provide a significant quality-of-life improvement for a wide range of Android users. From Pixel owners, for whom the app is a default, to those using other handsets, the ability to prevent in-call screen rotation has a direct and positive effect on daily use. It eliminates a notable point of friction that previously complicated one of the most basic functions of a smartphone.
A prime use case is preventing disorientation during critical call functions. For instance, in a professional setting where a user needs to quickly end one call to join another, the assurance that the hang-up button will be in its expected location is invaluable. This update removes a layer of unpredictability, restoring confidence and efficiency to the fundamental act of making and receiving phone calls.
Challenges and Implementation Hurdles
Despite the update’s success, the technology faced certain challenges in its rollout. A significant technical hurdle was its initial availability, which was limited to a beta version of the app (v. 202). This staggered release model, common in software development, means that the solution was not immediately accessible to all users experiencing the problem, delaying its widespread adoption and temporarily fragmenting the user experience.
Moreover, a key obstacle to its effectiveness is user awareness. The “Keep portrait mode on calls” feature is not enabled by default; it requires users to navigate into the app’s settings to activate it. Many users who are less technically inclined or unaware that a fix exists may continue to struggle with the rotation issue, highlighting the challenge of ensuring that optional, user-activated solutions reach the entire intended audience.
Future of the Google Phone App
This update provides an insightful outlook on where the technology is heading. Based on this user-centric precedent, it is reasonable to expect more user-requested customization options to be integrated into the Phone app and other core Google applications. Future developments may include greater control over call screen layouts, notification handling, or integration with other services, all driven by community feedback.
In the long term, this approach may have a profound impact on the Android ecosystem as a whole. By consistently prioritizing user control and responding to specific pain points, Google could further solidify Android’s reputation as a flexible and adaptable operating system. This philosophy of co-creation with the user base has the potential to become a defining feature of the platform, fostering loyalty and driving innovation from the ground up.
Conclusion and Overall Assessment
The review of this Google Phone app update concluded that it was a highly effective and necessary solution to a widespread user complaint. The introduction of a dedicated toggle to lock screen orientation during calls directly addressed a significant usability flaw without compromising other system-level functionalities. This change was praised for its simplicity and its direct impact on improving the core user experience.
Ultimately, the update stood as a prime example of a developer listening to and acting on community feedback. It reaffirmed that even minor adjustments, when targeted correctly, can produce a major positive impact on daily usability. The technology’s implementation was a successful case study in user-driven design, demonstrating a commitment to refinement that strengthens the relationship between a platform and its users.