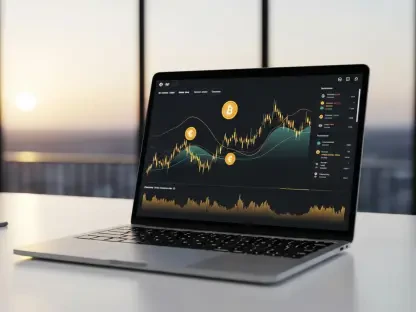
In a recent study, the use of smartwatches was linked to significant improvements in physical activity levels among people with type 2 diabetes, a condition affecting millions worldwide. Staying physically active is essential for managing this disease as it helps regulate blood sugar, enhances cardiovascular health, and improves overall quality of life. However, about 90% of individuals with type 2 diabetes do not meet the recommended levels of physical activity, often due to low motivation or uncertainty about safe exercise regimes. This study, with participants from the UK and Canada, explored how wearable technology paired with remote coaching could serve as a catalyst for long-term behavioral change.
The study involved 125 adults aged 40 to 75 who had recently received a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Each participant collaborated with an exercise specialist to develop a personalized six-month physical activity plan aimed at gradually increasing moderate-to-vigorous exercise and daily lifestyle activity. This study was designed to overcome common obstacles such as lack of motivation and uncertainty about safe activities, showcasing how technology can effectively support behavior change in healthcare. These personalized plans, complemented by remote support through phone or video calls, demonstrated the potential of combining technology and human intervention to support healthier lifestyle choices.
Revolutionary Role of Wearable Technology
This innovative research revealed that smartwatches could significantly influence physical activity engagement. Participants utilizing wearable technology in conjunction with their activity plans were remarkably ten times more likely to embark on their workout regimes compared to those solely relying on remote coaching. Moreover, those with smartwatch assistance were seven times more likely to maintain their activity levels after six months, highlighting the enduring impact of technology on fostering healthier habits.
The smartwatches used in the study were equipped with movement and heart rate sensors and paired with a mobile app for real-time activity tracking. Participants received personalized text messages based on their progress and had the opportunity to communicate directly with their coaches. Real-time feedback and the ability to adjust activity plans fostered a sense of engagement and accountability. This setup ensured that the wearable device was not just a passive tool but an active participant in each individual’s journey toward better health. The striking outcomes of this component of the study underscore the importance of integrating technology creatively and purposefully into health interventions.
Sustained Benefits and Empirical Evidence
The findings of the study were overwhelmingly positive, with notable long-term benefits observed even after formal support concluded. Over half of the participants equipped with smartwatches were meeting the recommended activity levels at the program’s end, compared to a mere 17% in the control group. This demonstrated a remarkable increase in adherence to physical activity recommendations among those with wearable technology support. Feedback from participants underscored that the flexibility of activity plans and personalized notifications from their devices served as strong motivators, proving that technology can be an effective ally in addressing common barriers to physical activity.
These results align with growing empirical evidence supporting the use of wearable technology to encourage sustained physical activity across diverse populations. A review and meta-analysis in 2022 of more than 160 randomized controlled trials reinforced the effectiveness of fitness trackers in promoting physical activity, showing an average increase of approximately 1,800 steps per day. These studies collectively suggest that wearables, when combined with personalized feedback or behavior-change support, can serve as powerful tools for fostering long-term commitment to physical activity goals, both in individuals with diabetes and the broader population.
Effective Strategies for Maximizing Wearable Benefits
Given the proven benefits of smartwatches in promoting fitness, applying strategies that maximize their advantages is essential. Setting realistic, specific fitness goals is crucial, with research indicating that breaking down broad intentions into more manageable tasks aids in maintaining motivation and preventing feelings of being overwhelmed. Scheduling activities with reminders or calendar prompts helps build familiarity and reduces the likelihood of missed workouts. Progress tracking is another key strategy, boosting motivation by allowing individuals to see tangible progress and enhancing accountability.
Additionally, incorporating small rewards helps reinforce progress. Many devices offer features like badges or streaks, celebrating small wins and encouraging users to persist. Sharing progress with friends or coaches can boost commitment by increasing motivation and providing external encouragement. It’s important to remember, however, that the tracker is a tool, not a solution. Its true value comes from how it supports individual goals and assists in building long-term habits, enhancing motivation and self-belief.
Future Considerations for Wearable Technology
A recent study found that using smartwatches can significantly boost physical activity levels in people with type 2 diabetes, a condition impacting millions globally. Staying active is crucial for managing this disease as it aids in controlling blood sugar, promotes cardiovascular health, and enhances overall quality of life. Yet, around 90% of those with type 2 diabetes fall short of recommended physical activity levels, often due to low motivation or uncertainty about safe exercise options. This study, with participants from both the UK and Canada, examined how wearables, combined with remote coaching, could trigger long-term behavioral changes.
The research included 125 adults aged 40 to 75, recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Participants worked alongside an exercise specialist to create personalized six-month activity plans, focusing on gradually increasing moderate-to-vigorous exercise and daily activities. The study aimed to tackle common barriers such as low motivation and confusion about safe exercises, highlighting the effectiveness of technology and human support in fostering healthier lifestyle choices.